String in Python
Any
values provided by the user in single quote ‘’ or double quote “” compiler
treats as string
Syntax
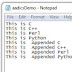
Firstname="Rupesh"
String
Manipulation functions
string.ascii_letters
string.ascii_lowercase
string.ascii_uppercase
string.digits
string.hexdigits
string.letters
string.lowercase
string.octdigits
string.punctuation
string.printable
string.uppercase
string.whitespace
capitalize()
center(width,
fillchar)
count(str,
beg= 0,end=len(string))
decode(encoding='UTF-8',errors='strict')
encode(encoding='UTF-8',errors='strict')
endswith(suffix,
beg=0, end=len(string))
expandtabs(tabsize=8)
find(str,
beg=0 end=len(string))
index(str,
beg=0, end=len(string))
isalnum()
isalpha()
isdigit()
islower()
isnumeric()
isspace()
istitle()
isupper()
join(seq)
len(string)
ljust(width[,
fillchar])
lower()
lstrip()
maketrans()
max(str)
min(str)
replace(old,
new [, max])
rfind(str,
beg=0,end=len(string))
rindex(
str, beg=0, end=len(string))
rjust(width,[,
fillchar])
rstrip()
split(str="",
num=string.count(str))
splitlines(
num=string.count('\n'))
startswith(str,
beg=0,end=len(string))
strip([chars])
swapcase()
title()
translate(table,
deletechars="")
upper()
zfill
(width)
isdecimal()
String can be accessed based on index as well
in Python
print
firstname[0]
R
firstname="Rupesh"
print firstname[2:4]
pe
Escaping
Character
Escape
Meaning
\newline Ignored
\\ Backslash
(\)
\' Single
quote (')
\" Double
quote (")
\a ASCII
Bell (BEL)
\b ASCII
Backspace (BS)
\f ASCII
Formfeed (FF)
\n ASCII
Linefeed (LF)
\r ASCII
Carriage Return (CR)
\t ASCII
Horizontal Tab (TAB)
\v ASCII
Vertical Tab (VT)
\ooo ASCII
character with octal value ooo
\xhh... ASCII character with hex value hh...
Splitting
a string
·
split splits the string
using specific literal.
Ex:.
alphabet
= "a b c d e f g"
lstdata
= alphabet.split()
for
letter in lstdata:
print letter
Formatter
Syntax
%c character
%s string conversion via str() prior to
formatting
%i signed decimal integer
%d signed decimal integer
%u unsigned decimal integer
%o octal integer
%x hexadecimal integer (lowercase letters)
%X hexadecimal integer (UPPERcase letters)
%e exponential notation (with lowercase 'e')
%E exponential notation (with UPPERcase 'E')
%f floating point real number
%g the shorter of %f and %e
%G the shorter of %f and %E
String in Python
 Reviewed by Rupesh
on
04:13
Rating:
Reviewed by Rupesh
on
04:13
Rating:
 Reviewed by Rupesh
on
04:13
Rating:
Reviewed by Rupesh
on
04:13
Rating:










No comments: